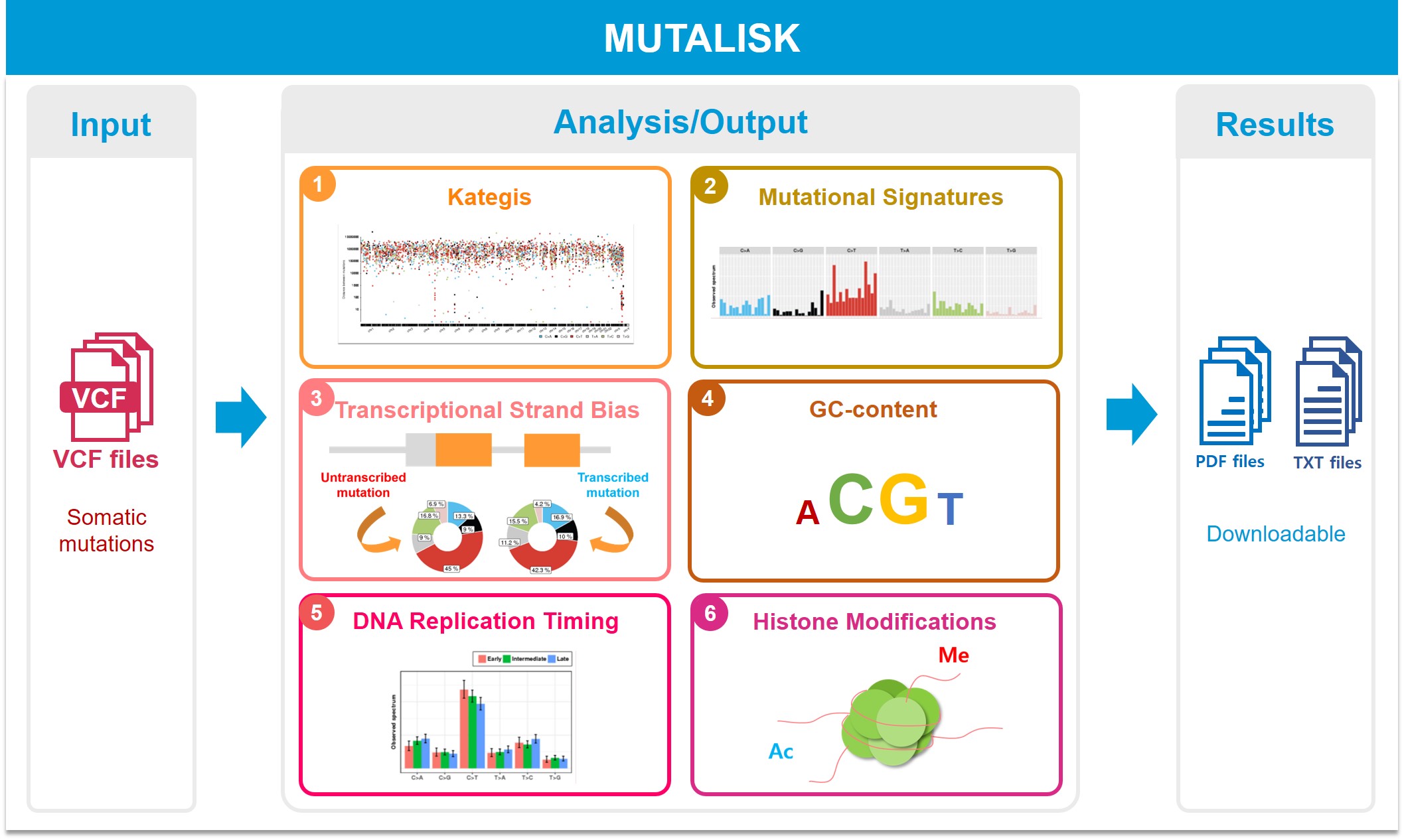
About the project
Mutalisk is a free and public web service program that enables comprehensive analysis of somatic DNA mutations with genome regulation elements and DNA sequence contexts.
Somatic DNA mutations are consequences of various non-random biological processes in somatic cells such as DNA repair and other endogenous/exogenous mutational processes. These mutations are not uniformly distributed genome-wide, but enriched in certain genomic loci, specific DNA sequence, and/or epigenome contexts according to the mutational processes.
Through elegant graphics and calculated statistics, this tool is designed to help researchers analyze the enrichment of somatic mutations and view potential causes of mutation rate variation for a list of somatic mutations. The input of the program is the standard vcf file, obtained from whole-genome/exome sequencing of single or multiple samples. Mutalisk performs the following analyses based on the mutations list:
A. Presence of regional hypermutation (Kataegis)
- Standard rainfall is introduced
B. Systematic decomposition of mutational signatures (COSMIC mutational signatures)
- Linear regression is used for the signature decomposition. Overfitting is controlled using Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC)
C. Associations between somatic mutation density and comprehensive genomic, epigenomic and transcriptional features including
- Transcriptional gene annotation
- Potential enrichments with more than ~10 different genomic elements such as replication timing and histone modifications (ENCODE project dataset)